Getters and setters are methods inside your classes. They are declared to save the data inside a class from being accidentally modified. For each variable in the class, the getter method returns its value and the setter method sets its value.
The name of a getter method starts with “get” followed by the variable name. Similarly, the name of setter method starts with “set” followed by the variable name.
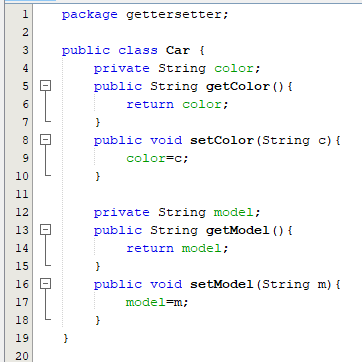
Consider a class named “Car”. The class will contain attributes “color” and “model” along with the getter and setter methods for both. The variables color and model will be declared private so that they can not be changed directly from outside the class and we will have public getter and setter methods to get and set their values from outside the class.
We will use the getter and setter methods to get and set the values of the variables instead of directly accessing them.
Getters and setters are not compulsory to use. You can use them according to your need. This is actually a concept that you can apply in other ways also.
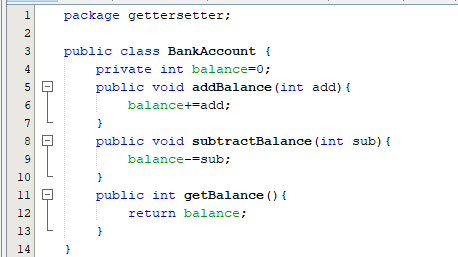
Let us consider a BankAccount class. It will have a variable balance and two methods addBalance and subtractBalance to change the balance. There will also be a getter method named getBalance to get the current balance. In this case, it is necessary to make the balance variable private so that it can only be modified by the addBalance and subtractBalance. If the balance gets changed without any record of adding or subtracting, it can cause problems. So, our BankAccount class will look like this:
Practice Corner:
- Create a class “Pet” with attributes: petType, name, age and color. Write getter and setter methods for each attribute.